Blooming Market Insights
Explore the latest trends and insights in digital marketing.
RFID: Tiny Tags, Tremendous Transformations
Discover how tiny RFID tags are driving massive changes across industries. Uncover innovations, benefits, and the future of this game-changing tech!
How RFID Technology is Revolutionizing Supply Chain Management
RFID technology is revolutionizing supply chain management by enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of inventory tracking. Unlike traditional barcodes, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. This technology allows for real-time visibility into inventory levels and locations, facilitating better decision-making for businesses. According to recent studies, companies that have implemented RFID systems have reported up to 30% reductions in inventory holding costs and improved order fulfillment times, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, the use of RFID technology streamlines various supply chain processes by minimizing manual errors and reducing labor costs associated with inventory management. With the ability to read multiple tags simultaneously, RFID systems enable businesses to perform inventory audits in a fraction of the time it would take using conventional methods. As a result, organizations are able to optimize their inventory levels and reduce stockouts or overstock situations. By adopting RFID technology, companies not only gain greater operational efficiency but also position themselves competitively in a rapidly evolving market.
Counter-Strike is a highly popular first-person shooter game that focuses on team-based gameplay and tactics. Players can choose to be part of the terrorist or counter-terrorist team, each with specific objectives. The game has evolved through various iterations since its initial release, with Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS:GO) being the most recent major version, introducing new maps, weapons, and modes. For those looking to explore options beyond typical gaming accessories, consider checking the Top 10 Alternatives to Bluetooth Trackers for enhanced convenience while gaming.
The Future of RFID: Innovative Applications Beyond Inventory Tracking
The future of RFID technology promises to revolutionize various industries beyond the traditional realm of inventory tracking. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, RFID systems are anticipated to play a crucial role in areas such as smart cities, healthcare, and supply chain transparency. For instance, in healthcare, RFID tags can streamline patient management by tracking the location of patients, medical equipment, and even medication. This can lead to enhanced patient safety and more efficient resource allocation, ensuring that healthcare providers have necessary tools readily available at a moment's notice.
Furthermore, RFID is set to transform the retail experience for consumers. Through the use of electronic shelf labels and smart fitting rooms, retailers can create a more interactive shopping environment. A recent trend involves integrating RFID with augmented reality applications, allowing customers to visualize how products would look or function in real life. This innovative approach not only enhances customer engagement but also optimizes inventory management by providing real-time data on product availability. As these technologies evolve, the potential uses for RFID seem limitless.
What is RFID and How Does it Work? A Comprehensive Guide
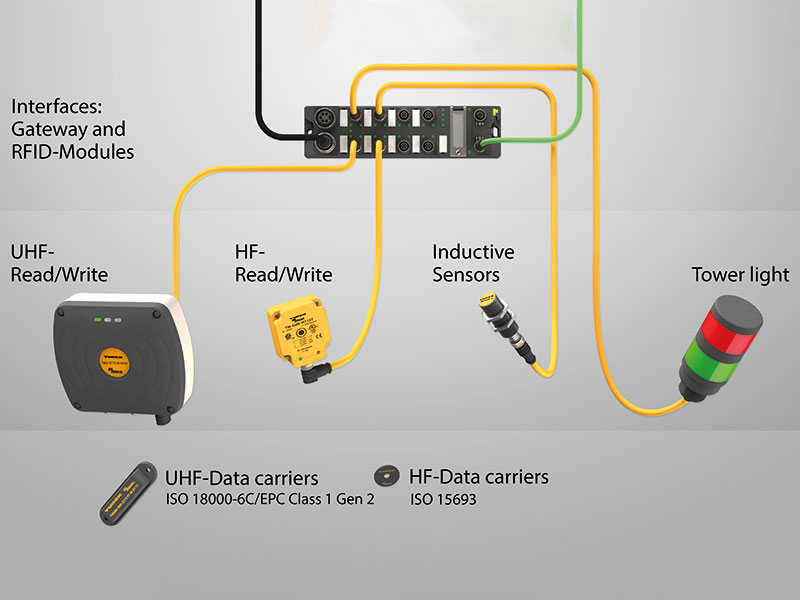
RFID, which stands for Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system comprises three main components: a reader, an antenna, and an RFID tag. The reader emits radio waves and receives signals back from the RFID tag. The tags can be passive, active, or semi-passive. Passive tags are powered by the energy from the reader's radio waves, while active tags have their own power source, allowing them to transmit signals over greater distances. This technology has gained popularity in various sectors, enabling efficient management of inventory, assets, and even personal identification.
How does RFID work? When an RFID tag comes within the range of an RFID reader, the reader sends out a radio signal that activates the tag. The tag responds by transmitting its unique identifier and other stored data back to the reader. This process occurs in milliseconds, allowing for real-time tracking and identification without the need for direct line-of-sight. RFID technology operates on various frequencies, including low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), and ultra-high-frequency (UHF), each with different read ranges and applications. From supply chain management to smart cards, RFID is increasingly becoming an integral part of our daily lives.